Amazon has created arguably one of the greatest loyalty programs in existence with Amazon Prime. When Prime was launched in 2005, it was intended mainly to subsidize shipping costs for Amazon customers. Over the years, it has evolved into a crucial part of Amazon’s business, as Prime customers are loyal and spend more on Amazon than non-Prime members. Access to services like Prime Video, Prime Photo, Amazon Music, and Prime Kindle, along with fast shipping of millions of products, has convinced over 100 million customers to happily pay the yearly membership fee—and Prime’s momentum doesn’t seem to be ebbing.
Prime on an Upward Growth Curve
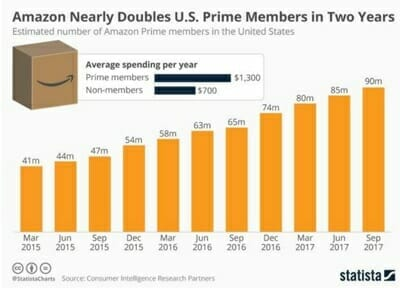
Despite the fact Amazon Prime has been growing at an accelerated rate, Amazon has not marketed the program in a manner to aggressively grow the subscriber base. Amazon also keeps the total number of Prime customers, and the markets they are found in, secret. Nevertheless, Prime customers are very important for Amazon’s long-term strategy, as they provide recurring revenue and enhanced channel loyalty—two of the hardest factors for an e-commerce channel to master.
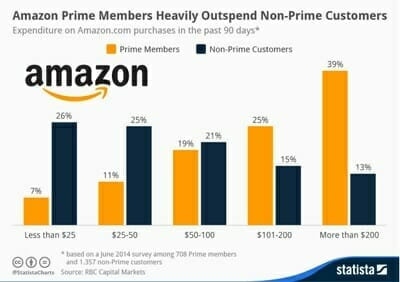
As mentioned previously, Amazon customers who are Prime members spend more. Data from Statista provides insight into the breakdown of these customers’ spending, showing that Prime customers spend multiples more per year than non-Prime customers.
Amazon is also making moves to generate more revenue from this already valuable program. In late April 2018, Amazon announced that they would be increasing the annual cost of Prime to new and existing members to $119, the first Prime price increase in four years. Although such a gambit always carries the risk of losing customers, many analysts believe that Amazon will face little pushback from clients based on the value the Prime program offers subscribers.
“The last time AMZN raised the price of Prime was in March 2014, & we do not expect the company to get much pushback from consumers given the increasing value of the service,” analyst Doug Anmuth wrote in April.
The Benefits of Prime
So what makes Prime so popular with Amazon customers—and its membership levels likely to withstand the coming price increase? Here are the key benefits that make Prime such an attractive proposition.
Exclusivity
Amazon Prime customers are the first customers to get access to new Amazon-branded devices. In fact, we are seeing growth in private label products that are only available to Prime customers. For non-Prime customers who desperately want a specific Amazon-branded product, the appeal may be adequate to motivate the purchase of an Amazon Prime membership.
Amazon also uses exclusivity in categories like video games to build new audiences that are very loyal. Amazon reserves access to purchase new game releases immediately for their Prime or Twitch Prime subscribers. Non-Prime or Twitch Prime customers who want to purchase these games are then forced to consider purchasing a membership in one of these programs to gain access to this sought-after merchandise.
Convenience
Amazon has changed what customers expect in terms of delivery speed and customer service. Prime customers expect to have their purchases inside two days and have little or no interaction with Amazon’s customer service team (an expectation that provides Amazon competitors like Walmart/Jet.com in the US and India’s Flipkart with a huge hurdle before they have even sold customers a single item.)
Being able to have faster shipping than non-Prime customers ensures that Prime customers become loyal to Amazon as they know from previous experience that their deliveries will arrive on time. This also ensures that these customers purchase products that Prime enabled as when they shop online or on mobile only see items that are able to ship fast.
On-demand product delivery can be seen as the ultimate form of convenience, and it’s something Amazon is attempting to provide their Prime customers with Prime Now, with a service that is even faster and more convenient than the normal Prime program. According to Amazon, Prime Now offers thousands of products across a variety of categories. Customers are also able to utilize restaurant and local store delivery in selected US cities.
While customers do pay more for delivery of items, these items can be delivered within two hours in select locations. The selection is much smaller than what’s available through Amazon’s normal Prime service, but when emergencies strike, customers want their products fast.
Amazon has used Prime Now as a market entry strategy in Singapore to leverage the mobile first dynamics of the Singapore market. With Prime Now, Amazon has also in a sense ensured that Uber, Postmates and other delivery services will have to battle them in the on-demand space.
Lower Prices
Prime customers save on two-day shipping costs on Prime eligible items. And in Amazon’s brick-and-mortar bookstores, Prime customers have been able to purchase books at the price seen on the Amazon website, whereas non-Prime customers pay the full recommended retail price. Having experienced this first-hand in Seattle, the urge to become a Prime member is much larger than what is seen when shopping online at Amazon.
Rewards
Amazon Prime customers are able to purchase products on Prime Day, a day Amazon created to feature (and sell more of) the Prime membership benefits—and it’s been hugely popular with customers. According to an Amazon press release regarding the Prime Day 2017 event, it grew by more than 60 percent compared to Prime Day 2016, with more new members joining Prime on July 11, 2017, than on any other day in Amazon’s history.
Another benefit of the Prime program is the 5 percent back on Amazon purchases that Prime customers get when paying with the Amazon Prime Rewards Visa Card or the Amazon Prime Store card. All Prime members also earn 2 percent rewards with Amazon Prime Reload when they reload an Amazon Gift Card Balance with their checking account.
These benefits help Amazon generate more sales, pay fewer fees on card transactions, and keep customer cash in the Amazon ecosystem.
Student Options
Amazon is one of the few online retailers that also provides a loyalty program for students. Prime Student is arguably one of the least spoken parts of Amazon’s Prime business, but its effects are significant: Amazon can lay its commercial claws on customers as soon as they enter college or university. Four years of Prime benefits during college certainly are likely to drive higher interest in lifelong Prime membership. Many of these new customers likely cost Amazon little to nothing to acquire, as the program may be an easy sell for parents who are regular Prime members and want their kids to enjoy the benefits of Prime while at school.
How Brands Can Capitalize on Prime
What must brands do to take advantage of the huge growth in Prime membership? The key is taking advantage of Prime eligibility for their products. Brands’ product listings can become Prime Eligible when they sell wholesale to Amazon (first party), or through third-party sellers that use FBA or Seller Fulfilled Prime for their shipping. Products that are Prime eligible perform better in Amazon’s search algorithm and show up higher in organic search results on the site. Meanwhile, customers are more likely to purchase Prime-eligible offers over non-Prime offers. We have seen firsthand how the shift to Prime eligibility can drive up customer conversion by 50 to 70 percent.
Prime is here to stay, and brands need to adapt to win in the Prime world. We have seen national brands lose share simply because they do not understand how critical Prime is to launching a top-selling product on Amazon. And we have seen small, unknown brands beat out larger national brands because the former understand how important Prime is to the Amazon flywheel today.

If you’re one of the estimated 20%–40% of brands who fire their agency annually, you can’t focus on that vision if you have to keep searching for the right support. BBE proudly retained >95% of our clients last year while applying focused dedication to our brand partners. If you’re ready to start over for the last time, contact us and find out why leading brands have partnered with us for so long.

